What do I observe the James Webb?

The James Webb, since its launch, has ceased to amaze us, from nebulae to infrared photos of our solar system.
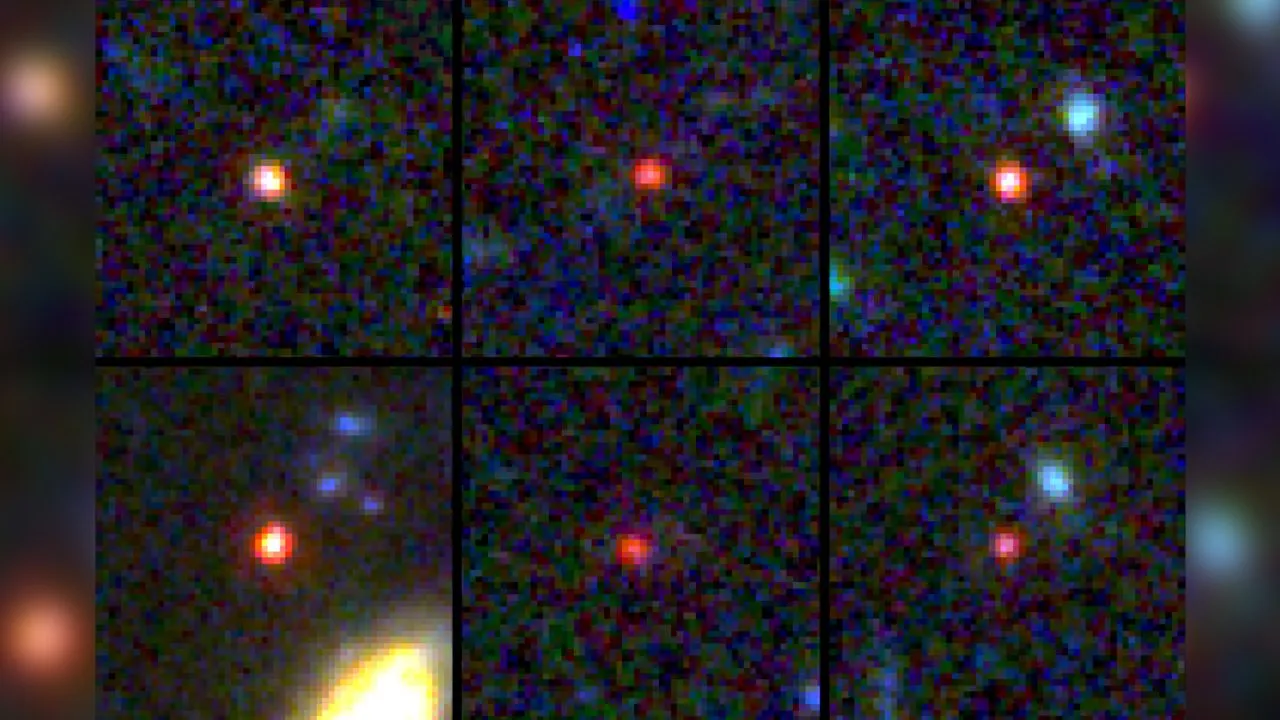
This time, the astronomers used the Webb to see beyond the obvious, and discovered something they did not expect, some six gigantic galaxies that existed between 500 and 700 million years after the Big Bang, according to the study published in the journal Nature.
These objects are larger than imagined, as they were expected to be small galaxies, quite young or not so large because they were among the first in the universe, but it was quite a discovery to see that there were mature galaxies at the beginning of time.
This was accomplished with James Webb’s infrared viewfinder, this light invisible to the human eye, but the Space Observatory is capable of detecting the faint light from stars and ancient galaxies.
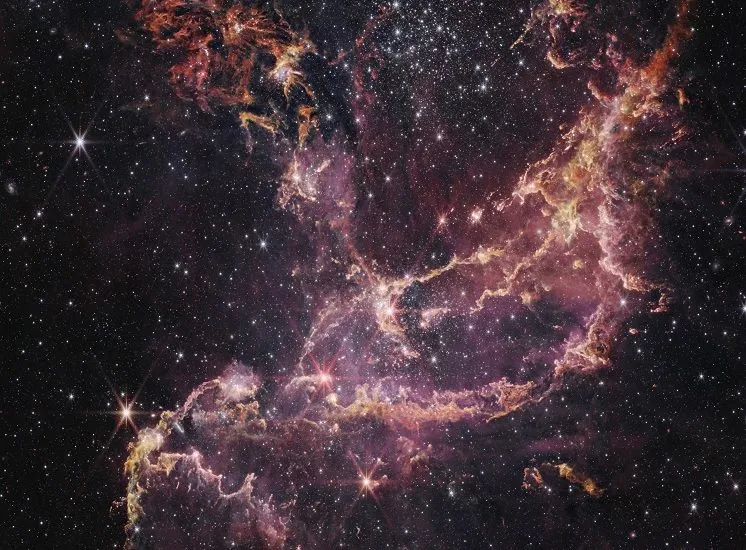

The James Webb can see up to 13,500 million years, something that is not a small thing, since according to some studies it is believed that the universe is 13,700 million years old, so in theory the space observatory has the capacity to see almost all the universe.
The fact that such large galaxies were formed at the beginning of the universe changes some concepts that were believed to be an affirmation, due to how gigantic they are, they broke many conceptions of the universe, which is why they are now nicknamed «universe breakers».
These galaxies conflict with 99% of the models that represent the earliest galaxies in the universe, which means that scientists have to rethink how galaxies formed and evolved, as galaxies are believed to have started as small clouds of stars. and dust that grew over time.
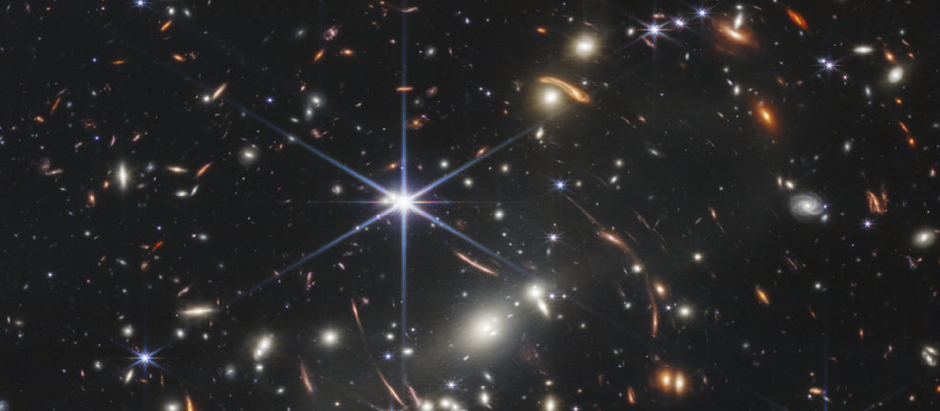

When these data were obtained, the scientists analyzed the images, the galaxies came out as points of light, something that did not convince the scientists, there seemed to be an error, and although they did not find one, it left them with a concern, a feeling that something was wrong. it fit.
Although there is the possibility that these primordial galaxies are not galaxies, but something else, opening the possibility that the objects we are seeing are not what we think we see.
For now, the data confirms that they could be super deep galaxies or black holes, this is due to the amount of mass they contain. That being said, some of the stars of more or less that period are 100 times larger than previously thought. so it is not so far-fetched to think of super-giant black holes, but it is something that can only be known with time.
And what do you think? Are these points of light galaxies? Are they black holes? It could be simpler, maybe the universe is older than we think.